Successful honey harvest requires skillful Apiary management. Which include application of knowledge and practices that will fully utilize the productive capacity of the honey-bee colony, managing low-producing colonies, placement of apiary, managing during various seasons’ i.e seasonal Apiary management etc. This good management will result into higher producing colonies and high productivity.
Some recommendations for Apiary managements are as under:
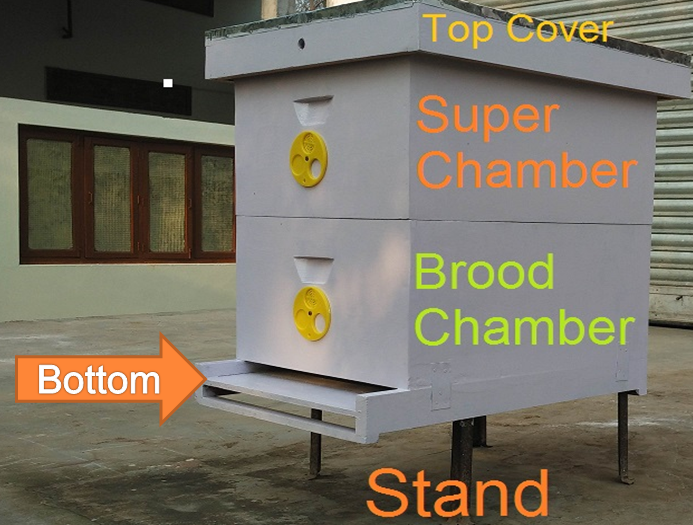
Standard bee hive
- Use of bee hive made as per BIS standard design- IS 1515: Beehives
- Use of Brood chamber nailed with the bottom board should be avoided
- Use of only wooden inner cover of right design over the brood / super chamber and never old gunny bag. The top cover should also be as per BIS design.
- Locally available seasoned lightweight wood to be used to make hives. Unseasoned wood should never be used
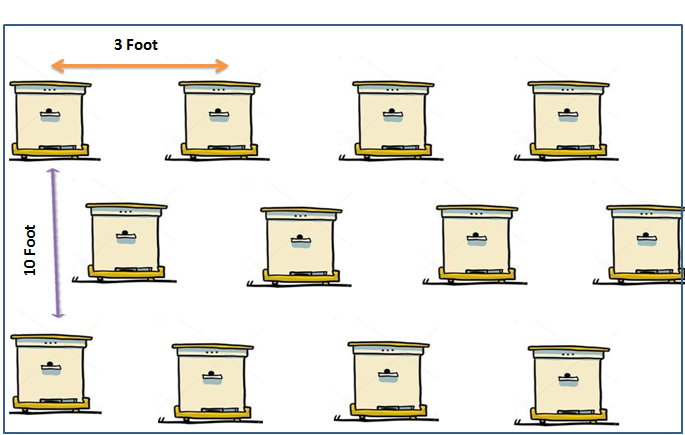
Placement of colonies in apiary
- In an Apiary, over-stocking of colonies should be avoided, either by restricting the number of bee colonies to be about 50-100 and/or by maintaining a distance of 10 feet and 3 feet from row to row and box to box respectively.
- Bee colonies should be well distributed over the nectar flow source / flowering crop for better Apiary management.
Placement of colonies in apiary
- In an Apiary, over-stocking of colonies should be avoided, either by restricting the number of bee colonies to be about 50-100 and/or by maintaining a distance of 10 feet and 3-5 feet from row to row and box to box respectively.
- Bee colonies should be well distributed over the nectar flow source / flowering crop.
Inspection of colonies
Precautions
- Inspection should be done on clear sunny days using proper protection tools.
- Avoid inspections during cold, windy and cloudy days in winter or higher hills and hot windy and rainy days in plains and hot weather.
- Personal hygiene that includes being free of any off smell or scent and scented oil on body or in hairs.
- Smoker to be kept ready for use whenever required to subdue the bees.
- Handling of healthy and diseased colonies separately.
- Handling of colonies should be gentle, avoiding jerks fast movements of hands. Crushing of bees should be avoided as it can cause stinging and spread of disease.
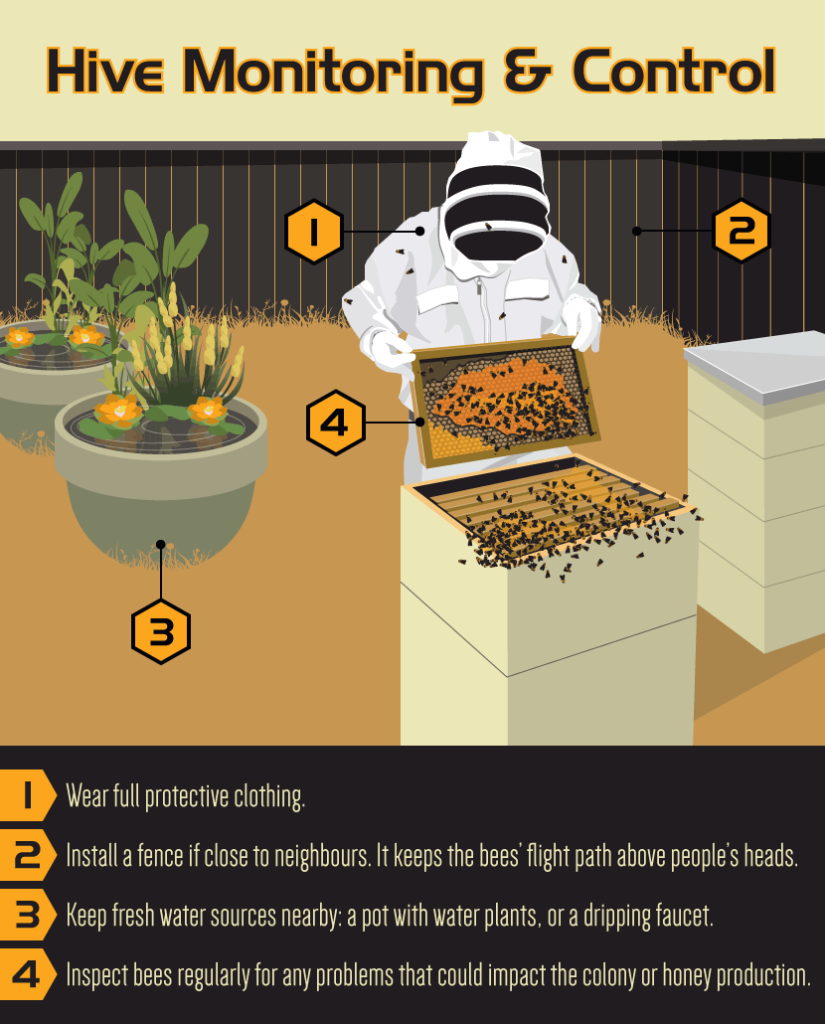
Following to be checked during inspection:
- Presence of a healthy laying queen; regular fresh eggs are the proof if queen is not seen due to rush of worker bees.
- Presence of regular larval and pupal (sealed) brood.
- Presence of enough food, honey and pollen for the bees and brood.
- Bottom board is clean and free of any debris or pest stages.
- Colony is free of any abnormality or infestation or diseased appearance or changes in behavior of bees.
Provision of fresh water in the apiary
For maintaining healthy bee colonies in the apiary, fresh water availability should be ensured, as water is used for the following:
- Maintaining adequate humidity that helps in proper incubation of eggs.
- Maintaining the temperature of the brood area /cluster between 35° and 37°C.
- Preparation of a mixture of honey and pollen of particular consistency (the bee bread) for feeding the brood by nurse bees.
Care in migration of the apiaries
Preparation for migration-
- Survey the area to assess the availability of the flora, safe location for placing the bee colonies, storing of accessories and dead stock, availability of fresh water source for bees, away from high ways, away from busy railway tracts, away from running (like river) or big water source, away from stagnated water safe from flooding possibilities, access to ease in transport etc.
- Ensure extraction of the honey to empty the supers completely and to lighten the brood chambers of the extra honey stock.
- Close the entrance gates of all the colonies. In the evening after sun set, when all the worker bees are inside.
- To avoid jerks pack the colonies internally (the frames in the hive bodies) and externally (bottom board to brood chamber to super to inner cover to top cover) properly.
During transport-
- In the vehicle, colonies should be packed in such a way that the entrance side should face the front side of the vehicle and the hives do not get jerks on any rough road.
- One should move the vehicle late in the evening after sun set and reach the destination within 10-12 hours about sun rise.
- Open the entrance gates only after the colonies are placed at their new locations.
- If the destination is far away, keep halting at intervals in day time, unload the hive and open the entrance gates at interim location and repeat the process of migration again.