Selection of good quality honey bees
Selection of good quality bees depending upon floral conditions and capability of investments beekeeping is done by either of two cavity dwelling species Apis cerena and Apis mellifera. However, quality of bees, particularly queen plays a major role in bee management.
Following recommendations on the selection of bee colonies:
- Stocks used to multiply honeybee colonies should be disease resistant, high honey yielding, young, healthy and of high egg laying capacity queen etc.
- Beekeepers should be well trained on the selection of good quality bees.
- Every beekeeper should keep record of his bee colonies and mark the colonies with above mentioned attributes for the purpose of multiplication of queens and new colonies.
- Beekeeper should replace the queens every second (two year old) year with the queen bred from selected colonies.
- Only disease free bee colonies to be bought from the existing beekeepers.
- To prevent inbreeding, capture few bee colonies from their natural abode in forests for further breeding/ multiplication or manage separate mating yards.
- Diseases free bee colonies should be bought from reliable and traceable source, which is traceable to its original beekeeper.
- It is recommended that the colonies of honey bees sourced should have high egg laying capacity queen, high honey yielding, young, healthy and disease resistant honeybees should be selected and reproduced.
- Colonies should be kept with good quality productive and prolific queen.
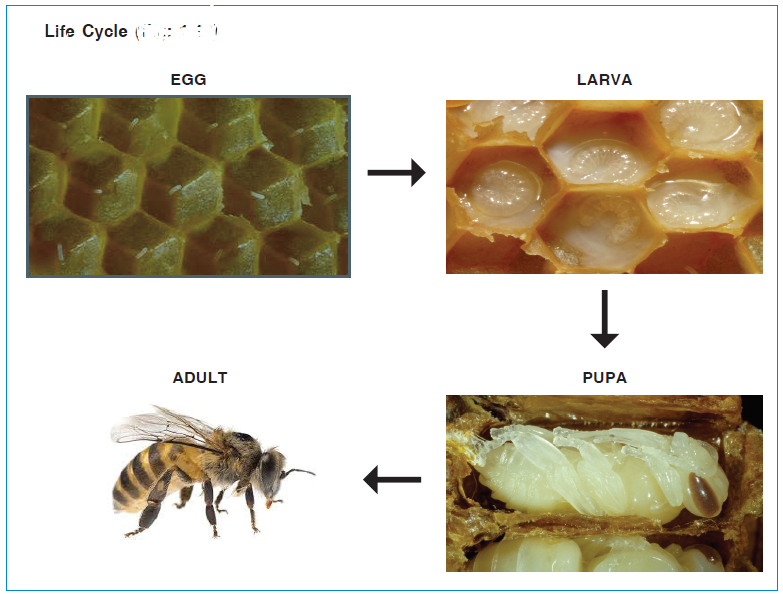
LIFE CYCLE OF HONEY BEE
A Honey bee life cycle has four main distinct stages or phases, egg, larva, pupa and finally an adult. The colonies of bees consist of three castes, Queen Bee, worker bee and drones (males). Queen bees lay eggs, worker bees are non-egg producing bees and drones are meant for mating purposes.

The total developmental time for a Queen bee is 16 days, 21 days for worker bee and approximately 24 days for drone or male bee.
Egg Stage
First stage of development in the life cycle is egg stage. Eggs are very minute and have appearance of poppy seeds in shape. Every egg has an opening on the broader side that enables a sperm to penetrate in. Hatching of eggs normally occurs after three days of egg laying.
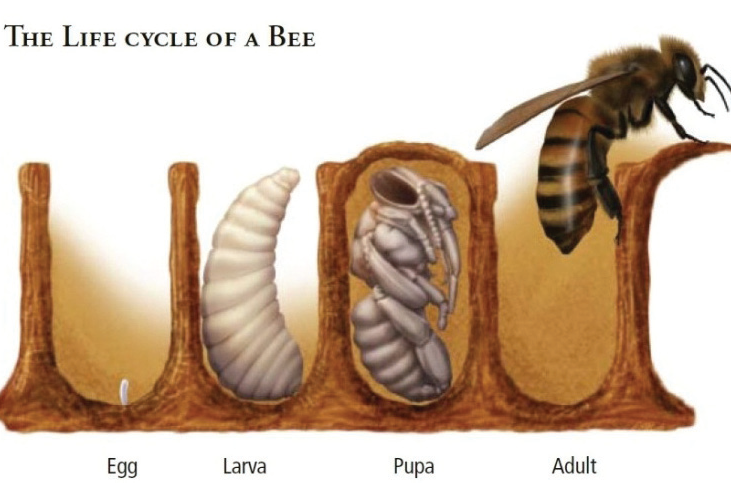
Larva Stage
This stage generally lasts up to nine odd days. During this stage, hatched larva is almost microscopic in size without legs and eyes. Larva is fed on a diet known as royal jelly for initial two days. As the third day progresses larvae that are destined to develop into queen bees continue to be fed on royal jelly, while worker larvae are fed on honey, water and pollens, called the bee bread. Larval stage for queen bee lasts for 5.5 days, 6 days for worker bees and 6.5 days for drones.
Pupa Stage
Reorganization of tissues massively takes place during pupa stage. Worm-like body has now three distinct parts of the body. This stage usually lasts for 7.5 days for queen bee, 12 days for worker bee and 14.5 days for drone bee (male bee).
Adult Stage
All three types of bees are now fully grown and are fully ready to accomplish their tasks. A typical colony of honey bee consists of 50,000 to 60,000 worker bees, 600 to 1000 drone bees and only 1 queen bee.